Know the differences between poor absorption, intolerance and allergy to lactose
Intolerance is a digestive problem, while allergy is an immune problem.
In the world, it is estimated that 60% to 70% of the population present some type of gastrointestinal discomfort after meals with food containing lactose. When this type of medical condition becomes routine, it can be a sign of the lactose intolerance development. Because it is a relatively new subject, there is much confusion between malabsorption x intolerance and milk protein allergy. So, let's break it down for better understanding.
Malabsorption is an inefficiency of the body in breaking down and transforming into simpler particles the lactose due to the low activity or absence of the lactase enzyme in the intestinal flora of the individual.
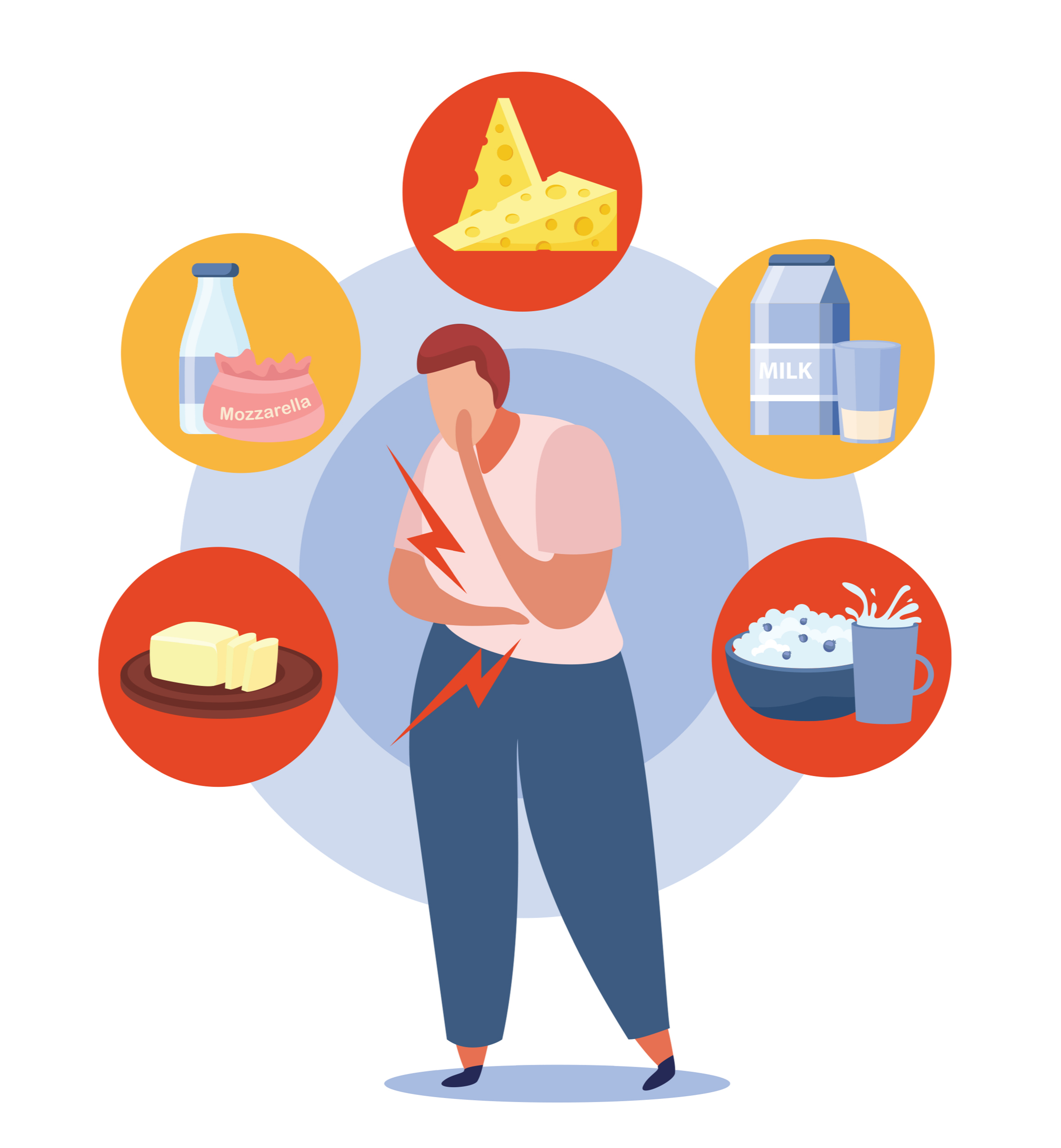

The inability to digest lactose completely or in parts is called lactose intolerance, which can be classified into three types:
- Primary hypolactasia – May occur due to the body's natural aging process. After the childhood, it is natural to have a decrease in the enzyme production.
- Secondary hypolactasia – It happens when the lactase production is affected by other already pre-existing diseases that triggers the imbalance (Chron's disease, celiac, irritable bowel syndrome and bacterial overgrowth).
- Congenital alactasia - Very rare. It is characterized by the non-production of lactase even in early childhood. In these cases, lactose should be cut off entirely from the diet for life.
On the other hand, malabsorption or hypolactasia may be the trigger for the lactose intolerance development, which is nothing more than the symptom of poor digestion in the gastrointestinal tract, with the onset of colic, gas pains, diarrhea and bloating after the consumption of dairy products. These discomforts appear due to insufficiency or deficiency of lactase. Without the enzyme, it is impossible for the body to break down the lactose particles in the small intestine. In this way, the sugar remains unchanged and goes to the large intestine, where it is fermented and consumed by bacteria, releasing gases (Hydrogen (H2) and generating discomforts.
Milk Allergy is classified as an immune reaction to milk protein, which manifests itself after the intake of a portion, however small, of milk or dairy products. That is, the immune system understands milk protein as a threat to the body and starts to generate reactions in order to expel the substance from the body, causing changes in the intestine, skin and respiratory system.
In other words, Intolerance is a digestive problem, while allergy is an immune problem. It is important to emphasize that because they have some very common and subjective discomforts, at the appearance of any one of them, you should seek a reliable doctor so that all the necessary tests are done and the discomforts are treated correctly.
And if you have any discomfort when consuming dairy products, click here and get to know Perlatte.